Source: Public Domain
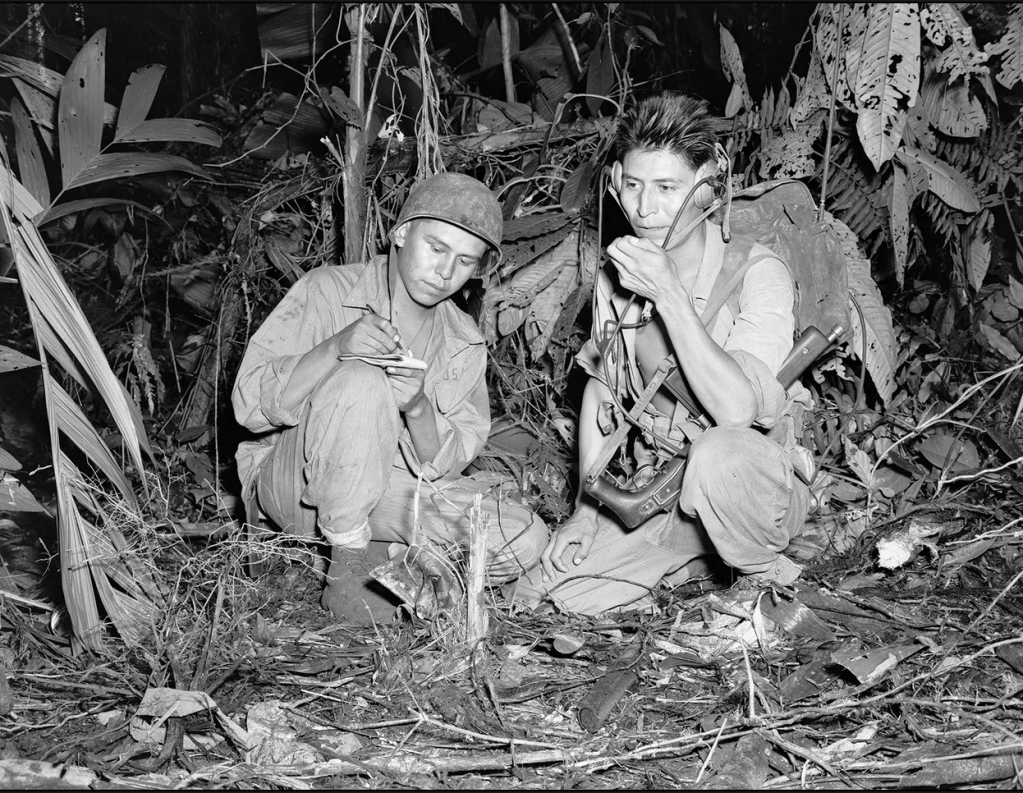
Code talkers were Native Americans from various tribes who were employed by the US military during World War 2 as radio operators; their native tongues were indecipherable to anyone listening in, and as a result, their transmissions of sensitive messages were invaluable in allied victories on every Pacific island, including Iwo Jima, as well as in Europe in decisive battles.
Codes were developed based on the languages of the Assiniboin, Cherokee, Cheyenne, Choctaw, Comanche, Cree, Crow, Fox, Hopi, Kiowa, Menominee, Navajo, Ojibwa, Oneida, Osage, Pawnee, Sauk, Seminole, and Sioux peoples. These men could transmit over open radio channels, knowing that the enemy would be unable to break their code. If a military term did not exist in their languages, a phrase was used in its place: A submarine became an iron fish; a fighter plane became a hummingbird; a squad became a black street. In all, throughout WW2, over 400 terms were developed and needed to be memorised by each code talker.
The code talkers continued to be used after the end of the war, which delayed their recognition by the wider public – until documentaries about their service finally began to emerge in the 1990s. In 2002, the U.S. Congress passed the Code Talkers Recognition Act, followed by a similar act in 2008 to honour the tribes who used their languages in the wartime service of the United States.
The use of code talkers was a socially complex one: The languages that were so invaluable to the US military were the very tools that the US government had been trying to eradicate in the name of cultural assimilation. Between 1880 and 1905, boarding schools were established, in which Native American children were taken from their families and educated; they were taught to reject their Native values, languages, traditions and anything to do with their native culture. They were punished, sometimes severely, for using their native tongues; they were forced to dress like the “white man”, and were not allowed to wear their native garments or have any vestiges of their tribes. Some 100,000 Native Americans were forced to attend such schools. Parents who resisted the kidnapping of their children were imprisoned; several from the Hopi tribe were even imprisoned on Alcatraz Island. Though most of these schools had been closed by the 1930s, the cultural and psychological damage had taken its toll on many native people groups, many of whom still struggle with their cultural identities today. At the time these young warriors were called into military service or chose to join after the bombing of Pearl Harbor, many were not even legal American citizens, yet they fought for their land and their families.
With that background in mind, the dedication and ingenuity of the code talkers are all the more astounding. They were often in the first wave of soldiers deployed as they were needed to pass on messages for the strategic planning and execution of driving back the Japanese from the Pacific islands. In addition to the Pacific arena, the European front also benefited from the code talkers’ ability to communicate directly with each other: Comanche code talkers were assigned to the 4th Infantry Division when it landed at Normandy in June 1944. In this context, some of the Comanche substitutes were turtle for tank, a pregnant bird for bomber, and crazy white man was their term for Adolf Hitler – a more insightful term has never been more aptly applied.
For a fascinating look into a history largely forgotten, please click on the following video recounting code talkers telling their stories firsthand as they return to the Pacific Islands with their families and find peace after decades of PTSD. The video is 1:10, but well worth the time when you can take it: Navajo Code Talkers of World War II (2018) | Documentary
Other sources:
https://eji.org/news/history-racial-injustice-cultural-genocide/